What Is an IPS Monitor? Monitor Panel Types Explained
If you’ve ever searched for a new computer screen, you’ve likely come across the term “IPS.” At this point, you might be wondering: What is an IPS monitor? And how do I know if it’s the right choice for me? Well, you’re not alone. With so many technical terms and specifications thrown around, shopping for a monitor can feel like navigating a maze of jargon.
But don’t worry—we’ve got you covered. Keep reading to discover why IPS monitors shine when it comes to color accuracy and viewing angles, or find the perfect one for your creative work here.
Before we get into the details, there are two key points you should know:
- IPS is one of the four main panel types used in monitors, alongside TN, VA, and OLED.
- All of these panel types fall under the broader category of LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology.
So, what does that mean for you? Simply put, the type of panel your monitor uses has a direct impact on how it looks, how fast it responds, and how versatile it is for different tasks. Gamers, graphic designers, and office workers all have unique needs, and different panel types cater to these needs in different ways.
Key Points: What Is an IPS Monitor?
- IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels deliver exceptional color accuracy and wide viewing angles—ideal for creatives and collaborative work.
- IPS monitors offer a strong balance between image quality and performance, with improved response times suitable for most users.
- Compared to other panels: TN is faster and cheaper (great for competitive gamers), VA has deeper blacks (great for movies), and OLED delivers the best visuals at a premium.
- IPS typically has lower contrast than VA and costs more than TN, but avoids color and angle distortion found in those panels.
- Bottom line: IPS is the most versatile choice for users who prioritize consistent, high-quality visuals across a range of tasks.
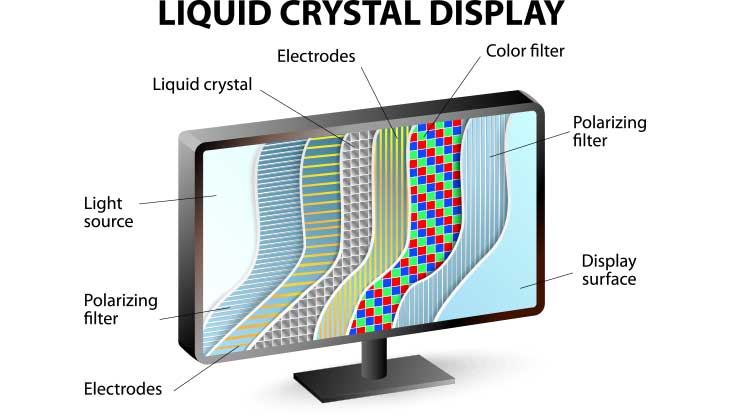
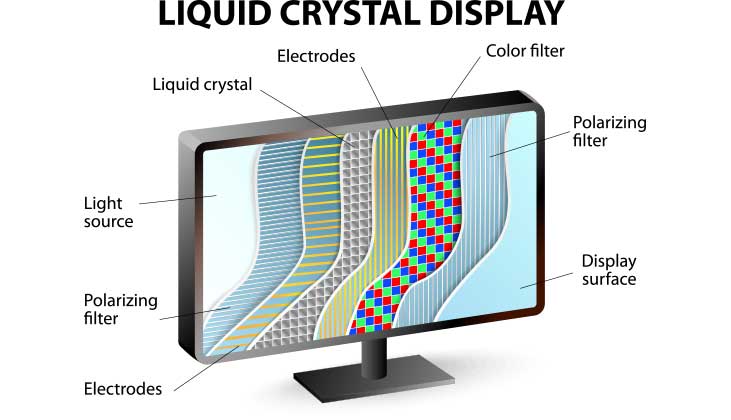
What Is an LCD Panel?
LCD, or “Liquid Crystal Display,” is a flat-panel display technology that uses thin layers of liquid crystals sandwiched between filters and electrodes. Unlike older CRT monitors that fired electrons at a glass surface, LCDs create images using a combination of backlights, liquid crystals, and filters. This approach results in thinner, lighter, and more energy-efficient screens, one of the reasons LCDs have become so widely used.
Why Use Liquid Crystals?
Liquid crystals (LCs) are unique materials that behave like both solids and liquids. Their ability to quickly twist when exposed to an electric current makes them perfect for controlling the amount of polarized light that passes through a display. This twist allows each pixel to adjust brightness and color in real time, which is essential for high-quality visuals.
How LCD Panels Work
Think of LCD like a window with adjustable blinds, twisting to control how much light passes through. Here’s a simple breakdown of the process:
- Backlight Turns On – This is the “sun” shining behind the blinds. It provides a constant source of light behind the screen.
- Light Becomes Polarized – The backlight produces unfiltered light, but LCD panels apply a filter to make it polarized. Polarized light means only specific light waves are allowed to pass through.
- Liquid Crystals Twist to Control Light – These liquid crystals are arranged in a rectangular grid and act like the “blinds” that open and close. When an electric current is applied, the liquid crystals twist to control how much of the polarized light gets through. This twisting process happens thousands of times per second, allowing LCD screens to display motion.
- Light Passes Through Color Filters – After the light passes through the liquid crystals, it hits the red, green, and blue (RGB) color filters, producing the full range of colors you see on screen.
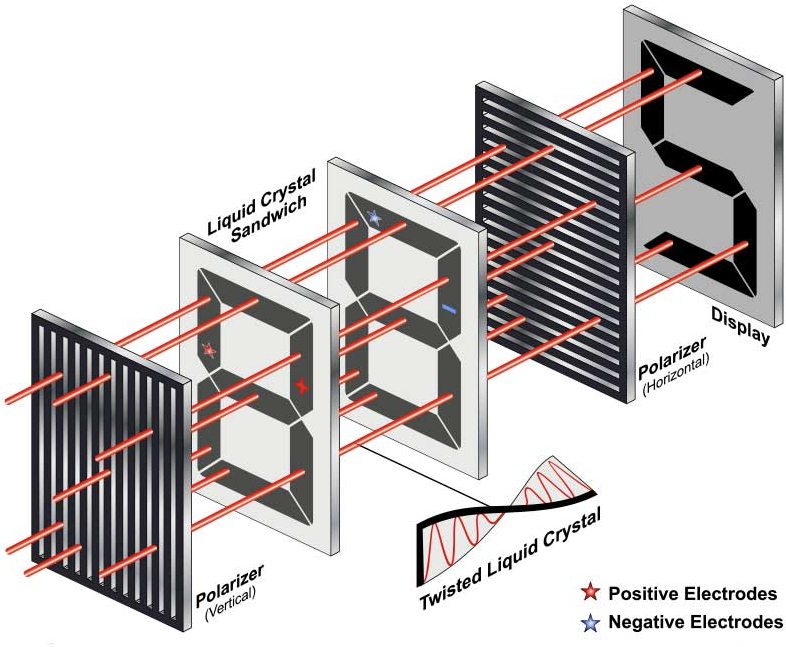
From Passive to Active Matrix
Early LCDs used passive-matrix technology, which controlled entire rows and columns of pixels at once. This approach was slow, causing blurry motion and ghosting, especially during fast-moving content like games or videos.
To improve performance, active-matrix technology was developed. Each pixel was equipped with its own TFT (Thin-Film Transistor), allowing for faster, more precise control. This breakthrough paved the way for the modern panel types we see today: IPS, VA, and TN.
What About LED Panels?
When browsing for monitors, you’ll often see the term “LED panel.” These aren’t a different display technology—they’re LCD panels that use LED (Light Emitting Diode) backlighting instead of older fluorescent backlights. LEDs produce brighter visuals with less energy and are essential for features like HDR (High Dynamic Range), which requires accurate color and bright white light. Because of this, LED-backlit LCDs have become the standard for most modern displays.
How Panel Type Affects Performance
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s dig into a key question: Why does the type of LCD panel matter so much?
Think of the panel type as your monitor’s personality. It shapes how your screen performs and plays a big role in deciding what it’s best suited for—whether that’s gaming, creative work, or everyday browsing.
What Panel Type Impacts
Each type of LCD panel influences a few core aspects of your display. Here are the key features that are directly affected:
- Response time and input lag: How fast the pixels change from one color to another, critical for gaming and fast-moving visuals.
- Viewing angles: The clarity and color accuracy you get when viewing the screen from the side.
- Color reproduction: How vivid, accurate, and true-to-life the colors look on the screen.
- Contrast ratio: The difference between the deepest blacks and brightest whites, crucial for watching movies or working with high-contrast visuals.
- Black levels: The depth and richness of dark scenes, which impact everything from cinematic content to creative work.
Each panel type — IPS, TN, VA, and OLED — has its own unique combination of these characteristics. While some people swear by one type over another, the truth is, there’s no “one-size-fits-all” solution, at least not without breaking the bank. It all depends on what you value most. Are you a competitive gamer who needs the fastest response time possible? Or are you a creative professional who prioritizes color accuracy and screen consistency?
Next, we’ll break down each LCD panel type and how it performs across these key categories, so you can find the right fit for your needs.
What Is an IPS Monitor?
IPS (In-Plane Switching) is a type of LCD panel technology known for its ability to deliver exceptional color accuracy, wide viewing angles, and consistent image quality. Unlike older TN (Twisted Nematic) panels, which struggle with poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, IPS panels offer a superior visual experience. This is achieved through the horizontal alignment of liquid crystals, which allows them to shift in unison, resulting in richer colors and enhanced visibility from multiple angles.
Over the years, IPS technology has seen multiple upgrades, each enhancing its performance. Variations like S-IPS, H-IPS, e-IPS, P-IPS, and PLS (Plane-to-Line Switching) have fine-tuned IPS’s already impressive capabilities. PLS, the most recent development, further improves efficiency and sharpness. While each version has its own unique features, they all share the same core strengths—superior color accuracy and ultra-wide viewing angles.
Why Creatives Choose IPS
These advancements have made IPS monitors the preferred choice for creative professionals like photographers, graphic designers, and media producers. Thanks to support for professional color spaces like Adobe RGB and DCI-P3, creators can trust that the colors they see on-screen will accurately represent the final product. The wide viewing angles also ensure that multiple people can review the screen without visual distortions — a key benefit in collaborative work environments.

What About Gaming?
You may have heard that IPS monitors aren’t ideal for gaming. Back in the day, IPS monitors had slower response times and lower contrast ratios, which led to motion blur during fast-paced scenes. But times have changed. Today’s IPS monitors have made massive improvements in response times, and many of them are now fast enough to keep up with modern gaming demands. As a result, more and more gamers are choosing IPS for the better color quality and viewing angles it provides.
That said, motion blur is still a common talking point. However, it’s not necessarily a big deal for all gamers, as opinions on the “drawbacks” of using an IPS monitor for gaming vary widely across the web. Here’s what one gaming technology writer had to say on the topic:
“As for pixel response, opinions vary. I personally think IPS panels are quick enough for almost all gaming. If your gaming life is absolutely and exclusively about hair-trigger shooters, OK, you’ll want the fastest response, lowest latency LCD monitor. And that means TN. For the rest of us, and certainly for those who place even a modicum of importance on the visual spectacle of games, I reckon IPS is clearly the best panel technology.”
Read the full article here.
IPS Monitors: The Bottom Line
When it comes to versatility, IPS monitors tick all the right boxes. With ultra-wide 178° viewing angles, stunning color accuracy, and steadily improving response times, they’ve become the go-to choice for a wide range of users. From graphic designers to photographers, video editors, and even gamers, an IPS monitor will offer a level of visual clarity that other panel types struggle to match.
Their ability to deliver wide, distortion-free viewing angles makes them a natural fit for a wide range of setups, so if you’ve ever compared an ultrawide vs. dual monitor setup or considered the benefits of curved vs. flat monitors, chances are you’ve already come into contact with an IPS panel.
IPS Monitor Advantages:
IPS Monitor Drawbacks:
- Below-average static contrast ratio
- “IPS Glow” – A faint white glow that appears when viewing dark content from sharp angles. This is mostly seen on lower-end or budget IPS models.
- More motion blur than in a TN monitor
Who Should Use an IPS Monitor?
What Is a Twisted Nematic Monitor?

TN monitors (short for “Twisted Nematic”) are the oldest LCD panel types around. Known for being affordable and fast, TN panels cost less than their IPS and VA counterparts, making them a popular choice for budget shoppers and entry-level, multipurpose monitors and laptops.
Why Gamers Like TN
But TN panels aren’t just for saving money. They’re also a top pick for competitive gamers. Why? TN panels offer blazing-fast response times and the highest refresh rates on the market. This means less motion blur and fewer screen-tearing issues during fast-paced games—a huge advantage over IPS and VA panels.
Where TN Falls Short
Of course, there are trade-offs, and for TN panels, it’s mostly about visuals. They struggle with:
- Narrow viewing angles (typically around 170° horizontal and 160° vertical), which can cause color and contrast shifts even when viewed head-on on larger screens.
- Inconsistent color accuracy makes them unsuitable for photo editing, graphic design, or any color-critical work.
- Noticeable distortion when viewed off-center, especially compared to a VA or IPS monitor that maintains image quality at wider angles.
This is why TN monitors aren’t recommended for color-critical work like graphic design and photo editing that benefit from wider viewing angles, higher contrast ratios, and better color accuracy.
TN Monitors: The Bottom Line
If you’re a competitive gamer or simply need a fast, affordable monitor for everyday tasks, TN panels still hold up. Just be aware of their limitations, especially if your work or play demands more accurate, vibrant visuals. For raw speed and value, though, TN still gets the job done.
TN Monitor Advantages:
- Rapid response time
- Affordable pricing
- Sufficient contrast for general use
TN Monitor Drawbacks:
- Most restrictive viewing angles
- Not recommended for color-critical applications
Who Should Use a TN Monitor?
- Gamers
- Budget-conscious users
- General users
What Is a Vertical Alignment Monitor?

Designed to overcome the limitations of TN panels, Vertical Alignment (VA) monitors deliver better contrast, richer colors, and wider viewing angles. You might encounter specific versions of VA technology, such as P-MVA, S-MVA, and AMVA (Advanced MVA), each with slight performance improvements. These high-end VA-type monitors can even rival an IPS monitor when it comes to professional-level color-critical applications.
Why Gamers Choose VA
One of the standout features of VA technology is that it is particularly good at blocking light from the backlight when it’s not needed. This allows VA monitors to achieve deeper blacks and higher static contrast ratios — often several times higher than other LCD technologies. This makes VA monitors great for enjoying videos and movies, as well as games focused on rich imagery (e.g., RPGs) rather than rapid speed (such as FPS games).
Contrast ratio is the measured difference between the darkest blacks and the brightest whites a monitor can produce. This measurement provides information about the amount of grayscale detail a monitor will deliver. The higher the contrast ratio, the more visible the detail.
VA Monitors: The Bottom Line
Thanks to advancements like MVA (Multi-domain Vertical Alignment), VA panels now offer the highest static contrast ratios of any LCD technology. This makes them a favorite for movie lovers, content creators, and gamers who want more visual depth and detail. Plus, for those who work in graphic design, video production, or photography, high-end MVA monitors provide consistent color accuracy and deeper, more vibrant images, making them a strong alternative to IPS panels.
VA Monitor Advantages:
- Wide viewing angles
- Outstanding contrast ratios
- Good response times
- Mid-range to high-end pricing options
VA Monitor Drawbacks:
- Slower response times vs. TN
- Contrast shift at extreme angles
Who Should Use a VA Monitor?
What Is an OLED Monitor?

OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) panels differ from the LCD panel types discussed above because they use positively/negatively charged ions to light up every pixel individually, unlike how LCDs use a backlight. This means that OLEDs avoid the screen glow (and create darker blacks) associated with LED backlights.
OLED Monitors: The Bottom Line
When it comes to picture quality, OLED is in a league of its own. With perfect blacks, vivid colors, and unparalleled contrast, OLED monitors deliver an experience that’s hard to beat. If you’re watching movies, playing visually rich games, or working on creative projects, OLED will make every detail pop.
However, with this premium quality comes a premium price. OLEDs are more expensive than TN, VA, or IPS monitors, and while the performance is exceptional, not everyone needs that level of perfection. If you’re just looking for a standard office monitor, an IPS, VA, or TN panel might be more practical.
OLED Monitor Advantages:
- Perfect blacks
- Vivid colors
- Super-Fast Response Times
OLED Monitor Drawbacks:
- Higher price
- Risk of burn-in
Who Should Use an OLED Monitor?
Choosing the Right Type of LCD Panel
Picking the right LCD panel isn’t about finding the “best” one—it’s about finding what works best for you.
If you’re looking for speed at a great price, TN panels are a solid choice. They offer the lowest cost and fastest response times, making them ideal for general use and fast-paced gaming.
Need deeper contrast and better viewing angles? VA monitors offer a nice step up. Their rich contrast and wide viewing angles make them a great fit for movie watching and immersive, visually-rich games.
But if color accuracy is your top priority—whether for photo editing or professional creative work—then an IPS monitor is the way to go. They’re known for their exceptional color performance and have become more affordable and widely available, making them a top pick for anyone seeking top-tier image quality.
Here’s a quick side-by-side to help you compare the key strengths of each panel type:
| Panel Type | Color Accuracy | Viewing Angles | Response Time | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLED | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | $$$$$ |
| IPS | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | $$$ |
| VA | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | $$ |
| TN | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | $ |
Final Thoughts
When it comes to picking the perfect monitor, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer — it all depends on your style, needs, and how you plan to use it. Whether you go for a budget-friendly TN panel, a high-contrast VA option, or a color-accurate IPS monitor, each one brings something unique to the table. And while panel specs matter, overall performance also comes down to build quality, internal components, and thoughtful design. Choose the monitor that fits you best, and you’ll be set for the long haul.
If you’re ready to see the IPS difference first-hand, explore our ColorPro SuperClear IPS monitors built for creative precision. Or, dive into how HDR monitors bring every detail to life.
Stay in the Loop
From bold ideas to exciting challenges, the ColorPro Newsletter is your front-row seat to everything happening in our creative community.